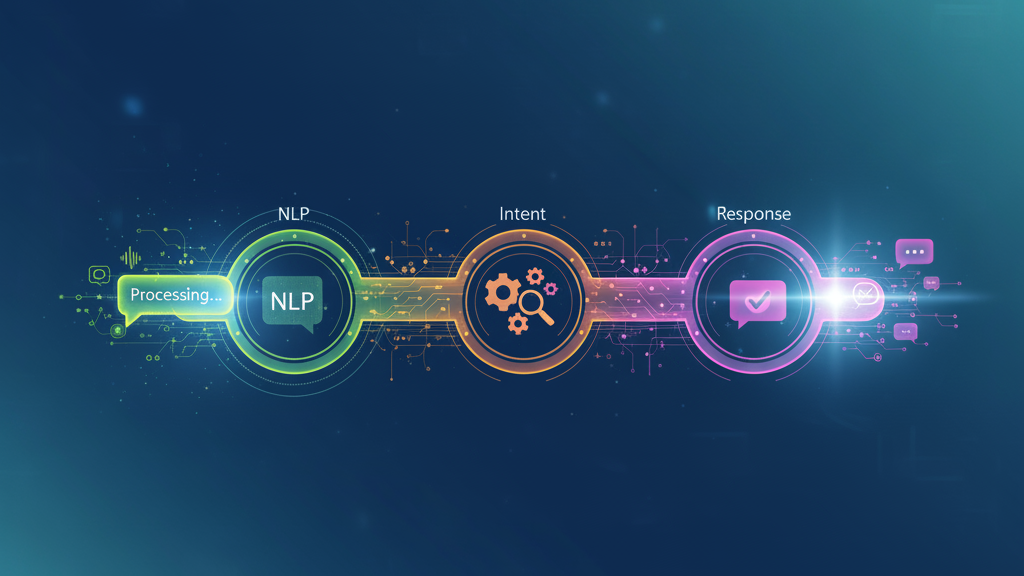
Chatbot replies may feel instant, but behind every quick response is a complex sequence of actions that unfold in milliseconds. Each message passes through several layers — analysis, interpretation, decision, and delivery. Understanding what happens behind the scenes reveals how modern chatbots transform raw text into meaningful, human-like conversation.
1. Message Input and Pre-Processing
When a user sends a message, the chatbot first receives and cleans the text. This step removes unnecessary characters, corrects formatting, and filters out noise such as typos, emojis, or symbols. The system may also detect the user’s language, flag inappropriate words, or perform basic spam checks.
Think of it as a message security gate — ensuring only clear, processable input moves forward.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Once the text is cleaned, NLP takes over. The chatbot breaks down the sentence into tokens (words or phrases), identifies key entities, and determines context and emotion.
Example: A user types, “I need help with my loan application.”
The NLP layer interprets “help” as the intent and “loan application” as the main subject. It also detects tone — neutral, urgent, or frustrated — to fine-tune the response.
This is how chatbots start to “understand” rather than just read.
3. Intent Detection and Matching
Here, the chatbot figures out what the user actually wants. It compares the processed message with its database of known intents (e.g., check status, book appointment, request refund).
If the intent match is strong, the bot retrieves or triggers the correct workflow. If the confidence score is low, it can ask clarifying questions or hand off to a human agent.
Intent matching is what makes the chatbot feel conversational rather than robotic.
4. Response Generation
Once the intent and context are clear, the chatbot decides how to reply. Depending on its design, it may: - Retrieve a pre-written answer. - Trigger an automated action (like checking an order status). - Generate a dynamic response through AI language models.
If integrated with databases or APIs, this is the step where it fetches live information before forming the reply.
5. Output Formatting and Delivery
The system converts the response into a readable message. It might include quick-reply buttons, rich text, or visuals. The chatbot then delivers the message back through the interface — often in under a second.
This stage is where the behind-the-scenes processing becomes visible to the user — a polished, timely reply that feels effortless.
6. Learning and Feedback Loop
After each chat, the system can log feedback and performance metrics. By analyzing which messages required escalation or were misunderstood, developers can refine NLP accuracy and expand the intent library.
This feedback loop is how chatbots grow smarter over time.
Conclusion
What looks like a simple conversation is actually a real-time data pipeline — cleaning, analyzing, predicting, and delivering results within seconds. By understanding this process, businesses can better appreciate what goes into making every chatbot interaction feel natural. Platforms like CuChat streamline this workflow, allowing SMEs to deploy powerful, intelligent chatbots without needing to understand every layer underneath.