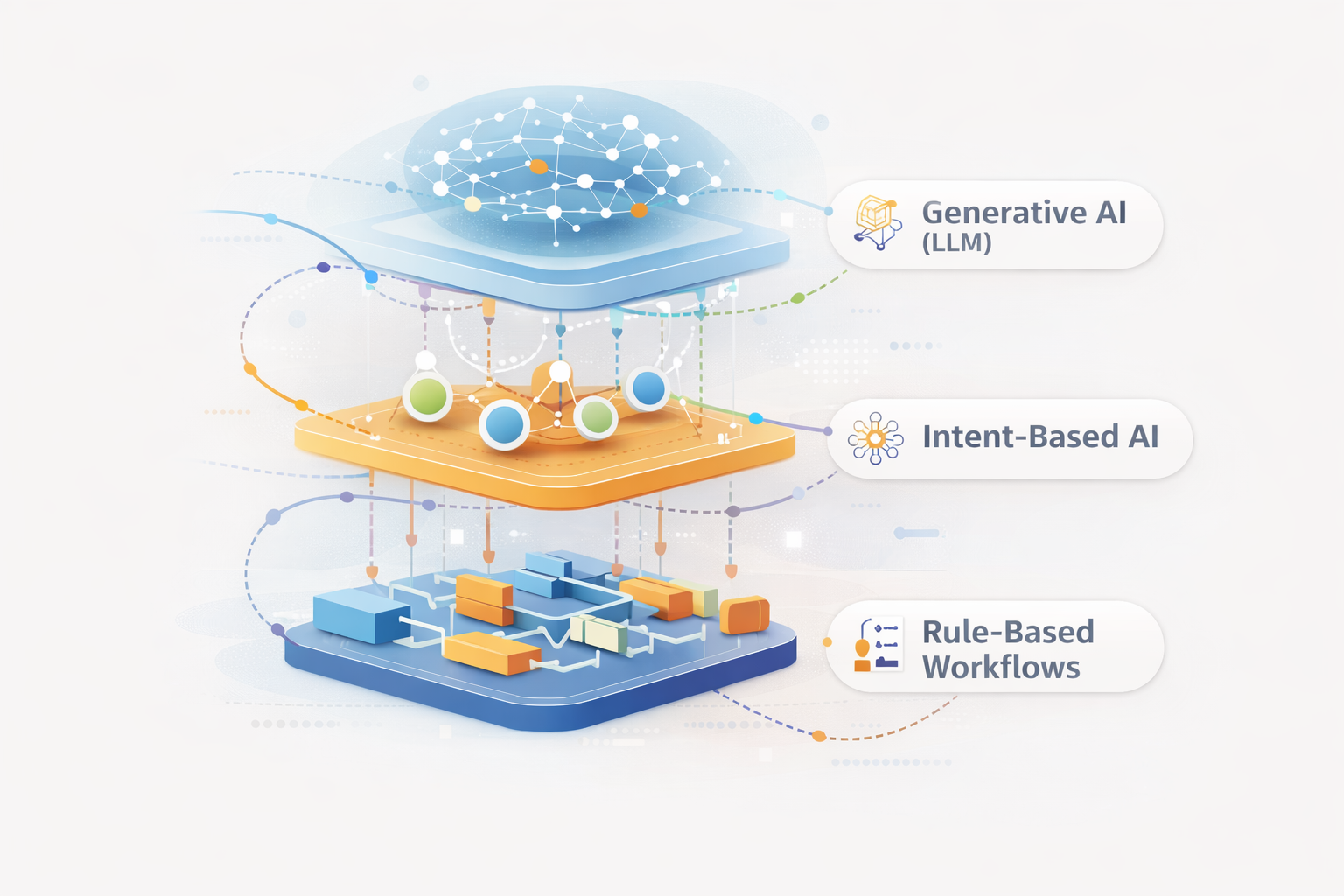
Introduction
Even the most advanced chatbots can fail — misunderstanding users, looping endlessly, or giving irrelevant answers. These failures rarely come from the AI itself; they stem from design flaws, outdated data, or missing escalation paths. Understanding why chatbots break helps businesses design smarter, more resilient systems.
1. Weak or Incomplete Training Data
Chatbots only perform as well as the examples they’re trained on. When the dataset is too narrow or repetitive, bots struggle to understand phrasing variations or synonyms. Over time, this leads to repeated “I don’t understand” loops.
How smart bots avoid it: They continuously learn from real user messages — expanding training data with every new interaction.
2. Poor Intent Architecture
When too many intents overlap, the chatbot can’t tell one request from another. For instance, “check payment” and “confirm payment” might confuse a weak intent setup.
How smart bots avoid it: They use clear intent structures, fallback logic, and distinct action triggers to reduce ambiguity.
3. Over-Automation Without Escalation Paths
Trying to automate every conversation often backfires. When bots attempt to answer beyond their scope, they frustrate users.
How smart bots avoid it: They include confidence thresholds — if uncertain, they escalate to a human instead of guessing.
4. Outdated or Static Knowledge Base
Information changes, but many chatbots don’t. Outdated FAQs or product details cause misinformation and loss of trust.
How smart bots avoid it: They sync with live data sources or scheduled updates to ensure accuracy.
5. No Feedback or Continuous Learning Loop
Without feedback analysis, a chatbot stays static — repeating the same mistakes.
How smart bots avoid it: They can be reviewed manually through chat logs to identify recurring gaps and improve coverage.